Why Is ARFCN Important in GSM and LTE Networks?
ARFCN (Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number) is a cornerstone of GSM and LTE network operations. It enables efficient frequency allocation, ensuring reliable communication across a mobile network. By assigning unique identifiers to radio channels, ARFCN plays a key role in managing spectrum resources, optimizing signal quality, and enhancing coverage. This guide explores how ARFCN functions in GSM and LTE technologies, its impact on performance, and its importance for preventing interference. By understanding ARFCN, network operators and engineers can ensure smoother network operations and an improved user experience.
What Is ARFCN and How Does It Function?
ARFCN forms the backbone of frequency management in GSM and LTE networks, enabling precise communication and efficient spectrum utilization.
Understanding ARFCN in Frequency Management
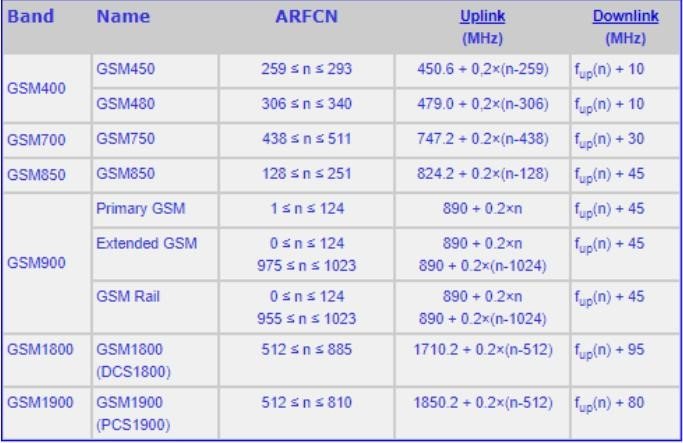
ARFCN is a unique identifier assigned to each radio channel within specific frequency bands. In GSM, ARFCNs are grouped by bands such as GSM900 (ARFCN 1–124) and GSM1800 (ARFCN 512–885). These identifiers help operators calculate the exact frequency of a radio channel, facilitating better management of the available spectrum. By defining frequencies clearly, ARFCN minimizes overlaps and ensures that channels operate efficiently.
How ARFCN Enables Network Communication
ARFCN ensures seamless communication between mobile devices and base stations. By assigning specific ARFCNs to channels, devices can connect to their designated frequencies without interference. This precise allocation allows the network to handle multiple connections simultaneously, maintaining efficiency and minimizing disruptions. The result is clear, uninterrupted communication for end-users and improved network reliability.
Why Is ARFCN Crucial for GSM and LTE Performance?
ARFCN significantly impacts the performance of GSM and LTE networks, from signal quality to data transfer speeds.
Role of ARFCN in Signal Quality and Coverage
Signal quality and coverage depend heavily on ARFCN allocation. By using ARFCNs effectively, operators ensure that each frequency channel delivers optimal signal strength. This results in wider and more consistent coverage, meeting user expectations for clear voice calls and stable data connections. Additionally, proper ARFCN distribution prevents signal degradation caused by interference, ensuring robust network performance.
ARFCN’s Impact on Data Transfer and Speed
In GSM and LTE networks, the assignment of ARFCN influences data transmission rates. Efficient allocation reduces congestion and maximizes throughput, enabling faster speeds and smoother data transfer. For LTE, where data demands are significantly higher, ARFCN plays a critical role in maintaining high-speed connections while supporting a large number of simultaneous users.
How Does ARFCN Support Frequency Allocation?
ARFCN facilitates efficient frequency allocation, which is essential for minimizing interference and maximizing network resources.
Preventing Interference Across Networks
ARFCN helps eliminate cross-channel interference by assigning unique identifiers to each frequency. This separation ensures that overlapping signals do not disrupt communication. For network operators, managing ARFCN effectively means fewer dropped calls, clearer audio quality, and more reliable data connections, even in densely populated areas.
Optimizing Network Resources with ARFCN
ARFCN allows operators to allocate their spectrum efficiently. By strategically assigning ARFCNs, they can balance load distribution and avoid overutilizing specific channels. This optimization enhances both network capacity and performance while reducing wasted bandwidth. Efficient ARFCN management also helps operators meet increasing data demands and maintain service quality.
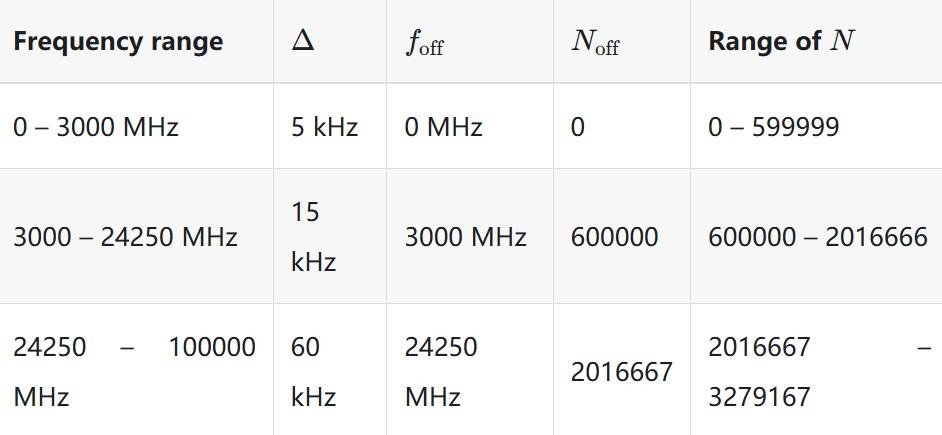
Comparing ARFCN in GSM vs. LTE Networks
While ARFCN is integral to both GSM and LTE, its application differs due to the unique demands of each technology.
Key Differences in Frequency Allocation
In GSM, ARFCN assigns specific frequencies to narrow bands such as GSM900 or GSM1800, making frequency allocation straightforward. LTE, on the other hand, uses a wider frequency range and employs techniques like Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) and Time Division Duplex (TDD). These methods require more complex ARFCN systems to manage broader bandwidths and multiple frequency bands efficiently.
Unique ARFCN Challenges in LTE
LTE networks must support higher data rates and more devices, which increases the complexity of ARFCN management. The coexistence of FDD and TDD adds another layer of complexity, requiring precise frequency planning to maintain network stability and performance. Despite these challenges, ARFCN remains essential for managing LTE’s advanced spectrum needs and ensuring smooth operation across all channels.
Conclusion
ARFCN is a vital component in GSM and LTE networks, enabling precise frequency allocation and seamless communication. By reducing interference, enhancing signal quality, and supporting high-speed data transmission, ARFCN ensures reliable network performance. Its role in spectrum management allows operators to optimize resources, improve coverage, and deliver better user experiences. As mobile networks continue to evolve, mastering arfcn management will be increasingly important for network engineers and operators striving to meet growing demands. Understanding and effectively deploying ARFCN can significantly enhance network operations, making it a cornerstone of modern mobile communication.